Kagatoni language: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
m (→Case) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
!colspan=2|[[Wikipedia:Trill consonant|Trill]] |
!colspan=2|[[Wikipedia:Trill consonant|Trill]] |
||
| |
| |
||
| − | | |
+ | |r |
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 150: | Line 150: | ||
===Nouns=== |
===Nouns=== |
||
| + | ====Case==== |
||
| − | Kagatoni nouns decline five grammatical cases: absolutive, oblique, genitive, ergative and instrumental. |
+ | Kagatoni nouns decline five grammatical cases: absolutive, oblique, genitive, ergative and instrumental. |
{| style="text-align: center" class="wikitable" |
{| style="text-align: center" class="wikitable" |
||
|+ Examples |
|+ Examples |
||
! rowspan="2" | |
! rowspan="2" | |
||
| − | ! colspan="2" | -p, -k |
+ | ! colspan="2" | Final -p, -k |
| − | ! colspan="2" | -t |
+ | ! colspan="2" | Final -t |
| − | ! colspan="2" | |
+ | ! colspan="2" | Vowel final (truncating) |
| − | ! colspan="2" | |
+ | ! colspan="2" | Vowel final (non-truncating) |
|- |
|- |
||
! Suffix |
! Suffix |
||
| Line 173: | Line 174: | ||
| ''imbuk'' |
| ''imbuk'' |
||
| ''-∅'' |
| ''-∅'' |
||
| − | | ''quhlit' |
+ | | ''quhlit'' |
| ''-∅'' |
| ''-∅'' |
||
| ''laṭka'' |
| ''laṭka'' |
||
| Line 218: | Line 219: | ||
| ''-qa'' |
| ''-qa'' |
||
| ''ṭo-'''qa''''' |
| ''ṭo-'''qa''''' |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | |||
| + | ====Number==== |
||
| + | Kagatoni distinguishes between singular and plural number. The plural is marked with the prefix ''(i)n-''. |
||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="text-align: center" class="wikitable" |
||
| + | |+ Examples |
||
| + | ! rowspan="2" | |
||
| + | ! colspan="2" | Vowel initial |
||
| + | ! colspan="2" | Voiceless stop initial |
||
| + | ! colspan="2" | Initial m- |
||
| + | ! colspan="2" | Other consonants |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | ! Prefix |
||
| + | ! Example:<br/>''osa'' ("bull") |
||
| + | ! Prefix |
||
| + | ! Example:<br/>''ṭan'' ("woman") |
||
| + | ! Prefix |
||
| + | ! Example:<br/>''miqna'' ("month") |
||
| + | ! Prefix |
||
| + | ! Example:<br/>''halga'' ("metal") |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | ! Plural |
||
| + | | ''n-'' |
||
| + | | '''''n'''-osa'' |
||
| + | | ''n-'' |
||
| + | | '''''n'''-ṭan'' |
||
| + | | ''im-'' |
||
| + | | '''''im'''-miqna'' |
||
| + | | ''in-'' |
||
| + | | '''''in'''-halga |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 232: | Line 264: | ||
====Questions==== |
====Questions==== |
||
| − | [[Category:Languages]] |
+ | [[Category:Languages]][[Category:Verethia]] |
Latest revision as of 05:16, 9 November 2025
| Kagatoni | |
|---|---|
| kagaṭonye zyna | |
| Pronunciation | [kagatʼoɲe ʑna] |
| Native to | Central Etzavazi Republic (Kagatonah) |
| Ethnicity | Kagatoni people |
Native speakers | ~38 million (4623) |
Crinat
| |
Early form | Old Kagatoni
|
| Verethian script | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
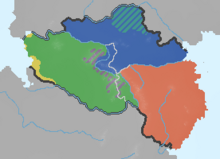 Languages of the Central Etzavazi Republic (areas where Kagatoni is the majority in red) | |
Kagatoni (kagaṭonye zyna [kagatʼoɲe ʑna]) is a Ćrinat language spoken in the Central Etzavazi Republic. As the national language of Kagatonah, it is one of three co-official languages of the Central Etzavazi Republic, alongside Talozhi and Mesvadi. Its closest relatives are Bachỹty and Socal.
History
Geographic distribution
Current status
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | (ŋ) | (ɴ) | ||
| Stop | Plain | p | t | k | q | ||
| Ejective | tʼ | kʼ | qʼ | ||||
| Affricate | Plain | t͡ɕ | |||||
| Ejective | t͡ɕʼ | ||||||
| Fricative | v | s | ɕ ʑ ç ʝ | h | |||
| Approximant | ʋ | l | j | ||||
| Trill | r | ||||||
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Close-mid | [e] | [ə] | [o] |
| Open-mid | ɛ | ɔ | |
| Open | [æ] | a | [ɑ] |
Kagatoni also has two diphthongs: /ɛi̯/ and /ɔu̯/.
Writing system
Grammar
Typical of Ćrinat languages, Kagatoni is an agglutinative language that relies heavily on affixation. It has a split-ergative morphosyntactic alignment, where nouns can exhibit ergative-absolutive or absolutive-oblique alignment depending on the sentence.
Verbs
Nouns
Case
Kagatoni nouns decline five grammatical cases: absolutive, oblique, genitive, ergative and instrumental.
| Final -p, -k | Final -t | Vowel final (truncating) | Vowel final (non-truncating) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suffix | Example: imbuk ("dog") |
Suffix | Example: quhlit ("bow") |
Suffix | Example: laṭka ("green (n.)") |
Suffix | Example: ṭo ("swamp") | |
| Absolutive | -∅ | imbuk | -∅ | quhlit | -∅ | laṭka | -∅ | ṭo |
| Oblique | -e | imbuk-e | -ʲe | quhli-tye | =e | laṭk-e | -ye | ṭo-ye |
| Genitive | -da | imbun-da | -ta | quhlit-ta | -da | laṭka-da | -da | ṭo-da |
| Ergative | -ka | imbuk-ka | -ka | quhlit-ka | -ka | laṭka-ka | -ka | ṭo-ka |
| Instrumental | -qa | imbuh-qa | -qa | quhlit-qa | -q | laṭka-q | -qa | ṭo-qa |
Number
Kagatoni distinguishes between singular and plural number. The plural is marked with the prefix (i)n-.
| Vowel initial | Voiceless stop initial | Initial m- | Other consonants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefix | Example: osa ("bull") |
Prefix | Example: ṭan ("woman") |
Prefix | Example: miqna ("month") |
Prefix | Example: halga ("metal") | |
| Plural | n- | n-osa | n- | n-ṭan | im- | im-miqna | in- | in-halga |
Syntax
Word order
Word order in Kagatoni follows a Verb-Subject-Object (VSO) order. For example, the sentence "I read a book" can be expressed as follows:
Qola
read
nei
1S.ABS
ihe
book-OBL