Kagatoni language
| Kagatoni | |
|---|---|
| kagaṭonye zyna | |
| Pronunciation | [kagatʼoɲe ʑna] |
| Native to | Central Etzavazi Republic (Kagatonah) |
| Ethnicity | Kagatoni people |
Native speakers | ~38 million (4623) |
Crinat
| |
Early form | Old Kagatoni
|
| Verethian script | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
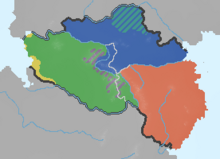 Languages of the Central Etzavazi Republic (areas where Kagatoni is the majority in red) | |
Kagatoni (kagaṭonye zyna [kagatʼoɲe ʑna]) is a Ćrinat language spoken in the Central Etzavazi Republic. As the national language of Kagatonah, it is one of three co-official languages of the Central Etzavazi Republic, alongside Talozhi and Mesvadi. Its closest relatives are Bachỹty and Socal.
History
Geographic distribution
Current status
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | (ŋ) | (ɴ) | ||
| Stop | Plain | p | t | k | q | ||
| Ejective | tʼ | kʼ | qʼ | ||||
| Affricate | Plain | t͡ɕ | |||||
| Ejective | t͡ɕʼ | ||||||
| Fricative | v | s | ɕ ʑ ç ʝ | h | |||
| Approximant | ʋ | l | j | ||||
| Trill | r | ||||||
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Close-mid | [e] | [ə] | [o] |
| Open-mid | ɛ | ɔ | |
| Open | [æ] | a | [ɑ] |
Kagatoni also has two diphthongs: /ɛi̯/ and /ɔu̯/.
Writing system
Grammar
Typical of Ćrinat languages, Kagatoni is an agglutinative language that relies heavily on affixation. It has a split-ergative morphosyntactic alignment, where nouns can exhibit ergative-absolutive or absolutive-oblique alignment depending on the sentence.
Verbs
Nouns
Case
Kagatoni nouns decline five grammatical cases: absolutive, oblique, genitive, ergative and instrumental.
| Final -p, -k | Final -t | Vowel final (truncating) | Vowel final (non-truncating) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suffix | Example: imbuk ("dog") |
Suffix | Example: quhlit ("bow") |
Suffix | Example: laṭka ("green (n.)") |
Suffix | Example: ṭo ("swamp") | |
| Absolutive | -∅ | imbuk | -∅ | quhlit | -∅ | laṭka | -∅ | ṭo |
| Oblique | -e | imbuk-e | -ʲe | quhli-tye | =e | laṭk-e | -ye | ṭo-ye |
| Genitive | -da | imbun-da | -ta | quhlit-ta | -da | laṭka-da | -da | ṭo-da |
| Ergative | -ka | imbuk-ka | -ka | quhlit-ka | -ka | laṭka-ka | -ka | ṭo-ka |
| Instrumental | -qa | imbuh-qa | -qa | quhlit-qa | -q | laṭka-q | -qa | ṭo-qa |
However, some nouns ending in vowels have an "inherent nasal", which reflects a former nasal vowel which was denasalized in all environments except before stops. This nasal is therefore absent from the absolutive case form, but present in all others. Hence, ha "sand" yields hanye, handa, hanka, hanqa instead of *haye, *hada, *haka, *haqa. Also as a consequence, polysyllabic nouns do not elide their final vowel; hence osa "bull" yields oblique osanye and instrumental osanqa instead of *ose and *osaq respectively.
Number
Kagatoni distinguishes between singular and plural number. The plural is marked with the prefix (i)n-.
| Vowel initial | Voiceless stop initial | Initial m- | Other consonants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefix | Example: osa ("bull") |
Prefix | Example: ṭan ("woman") |
Prefix | Example: miqna ("month") |
Prefix | Example: halga ("metal") | |
| Plural | n- | n-osa | n- | n-ṭan | im- | im-miqna | in- | in-halga |
Syntax
Word order
Word order in Kagatoni follows a Verb-Subject-Object (VSO) order. For example, the sentence "I read a book" can be expressed as follows:
Qola
read
nei
1S.ABS
ihe
book-OBL